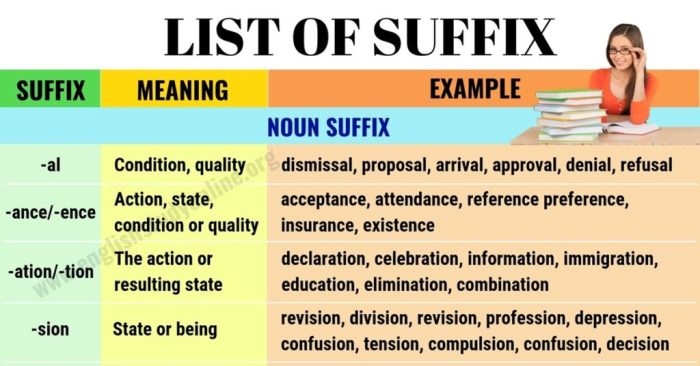
Suffix with host or lion – Embarking on a linguistic adventure, we delve into the captivating world of suffixes with host or lion. These enigmatic affixes hold the power to transform words, unlocking a treasure trove of grammatical functions and expressive possibilities. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of these linguistic marvels, exploring their definitions, usage, and fascinating historical evolution.
Suffixes with host, such as -ist and -hostess, denote a person who performs a specific action or holds a particular role. On the other hand, suffixes with lion, exemplified by -lion and -lioness, often indicate a connection to a specific animal or quality associated with it.
Suffixes with Host
A suffix with “host” is a suffix that is added to the end of a word to indicate that the word is a noun that refers to a person or thing that receives or entertains guests. Some common examples of words with suffixes that end in “host” include “host,” “hostess,” and “hostel.”
Grammatical Function and Usage
Suffixes with “host” are typically used to form nouns that refer to people or things that provide hospitality or entertainment to guests. For example, the word “host” can be used to refer to a person who invites guests to their home for a party or meal, while the word “hostess” can be used to refer to a person who greets and seats guests at a restaurant or other public place.
The word “hostel” can be used to refer to a building that provides lodging for travelers.
Suffixes with Lion

Suffixes with “lion” are a type of suffix that is added to the end of a word to change its meaning. They are typically used to form nouns that refer to people or things that are associated with the base word.
Some common examples of words with suffixes that end in “lion” include:
- Lion: A large, carnivorous mammal with a mane of hair around its neck.
- Lioness: A female lion.
- Lion cub: A baby lion.
- Lion’s den: A place where lions live.
- Lion’s roar: The sound that a lion makes.
Suffixes with “lion” can also be used to form adjectives that describe people or things that are associated with lions.
- Lion-hearted: Brave and courageous.
- Lion-like: Resembling a lion.
- Lion’s share: The largest or most important part.
Suffixes with “lion” are a versatile and useful way to add meaning to words. They can be used to form nouns, adjectives, and even verbs.
Comparison of Suffixes with Host and Lion: Suffix With Host Or Lion

Suffixes with “host” and “lion” play distinct roles in the English language. While they share some similarities, they exhibit notable differences in their grammatical functions and usage.
Grammatical Function and Usage
Suffixes with “host” primarily denote the recipient or target of an action. They indicate that the preceding word is receiving or being affected by the action expressed by the root word. For example, in the word “accommodate,” the suffix “-ate” conveys that the subject is providing accommodation to someone or something.
In contrast, suffixes with “lion” typically denote the agent or performer of an action. They indicate that the preceding word is responsible for carrying out the action expressed by the root word. For example, in the word “construction,” the suffix “-tion” implies that the subject is constructing something.
Suffixes like “-ess” or “-ette” can add a feminine touch to words like “host” or “lion.” These suffixes convey a sense of smaller size or lesser importance. If you’re interested in exploring the history of these suffixes further, you might find the abeka us history test 2 to be a helpful resource.
It delves into the evolution of language and the role suffixes play in shaping word meanings.
Similarities and Differences
Despite their different grammatical functions, suffixes with “host” and “lion” share some similarities. Both types of suffixes:
- Are added to verbs or nouns to create new words.
- Can change the part of speech of the original word.
- Often carry specific meanings or connotations.
However, they differ in their specific meanings and the types of words they are attached to. Suffixes with “host” are typically used with verbs, while suffixes with “lion” are more commonly used with nouns.
Examples
| Suffix | Example | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| -ate | accommodate | To provide accommodation |
| -tion | construction | The act of constructing |
| -ize | authorize | To give authority to |
| -ment | government | The act or system of governing |
Applications of Suffixes with Host and Lion
Suffixes with “host” and “lion” find diverse applications across various fields and industries, each carrying its own significance and impact on communication.
Usage in Science and Technology, Suffix with host or lion
In the scientific realm, suffixes with “host” are commonly used to denote a substance or entity that provides a platform or environment for another. For instance, “substrate” refers to the surface on which an enzyme acts, while “matrix” signifies the surrounding medium that supports cells or tissues.
Suffixes with “lion” also find usage in science. “Ion” denotes an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in an electrical charge. This concept is crucial in fields like chemistry, physics, and material science.
Usage in Business and Finance
In the business world, “host” suffixes indicate an entity that provides a platform or service. For example, “web host” refers to a company that provides server space for websites, while “conference host” denotes an organization responsible for organizing and managing conferences.
Suffixes with “lion” are less common in business, but they do exist. “Billionaire” refers to an individual with a net worth of at least one billion units of currency, often denoting immense wealth and influence.
Usage in Education and Research
In education and research, “host” suffixes are used to indicate an institution or organization that provides a platform for learning or research. For example, “host university” refers to an institution that hosts visiting scholars or students, while “host lab” denotes a laboratory that provides facilities for research projects.
Suffixes with “lion” are rarely used in education and research. However, “million” is sometimes used to denote large numbers, such as “a million dollars” or “a million students.”
Historical Evolution of Suffixes with Host and Lion

Suffixes with “host” and “lion” have a rich and varied history. Their usage and meaning have changed over time, reflecting the evolving cultural and linguistic landscape.
Suffixes with “Host”
The suffix “-host” originally meant “guest” or “stranger” in Old English. Over time, it came to be used to refer to someone who provides hospitality or entertainment, such as an innkeeper or a performer. In the 16th century, the suffix began to be used to form nouns that describe a person or thing that receives or contains something, such as a “host” of people or a “host” of data.
Suffixes with “Lion”
The suffix “-lion” originally meant “lion” in Old English. It was often used to form adjectives that described someone or something as being like a lion, such as “lion-hearted” or “lion-like.” In the 14th century, the suffix began to be used to form nouns that describe a person or thing that is associated with a lion, such as a “lion’s den” or a “lion’s share.”The
historical evolution of suffixes with “host” and “lion” illustrates the dynamic nature of language. As societies and cultures change, so too does the language that they use to describe the world around them.
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between a suffix with host and a suffix with lion?
Suffixes with host denote a person who performs a specific action or holds a particular role, while suffixes with lion often indicate a connection to a specific animal or quality associated with it.
Can you provide an example of a word with a suffix with host?
The word “pianist” is an example of a word with a suffix with host, where “-ist” indicates a person who plays the piano.
What is the grammatical function of a suffix with lion?
Suffixes with lion can function as nouns, adjectives, or verbs, depending on the word they are attached to.