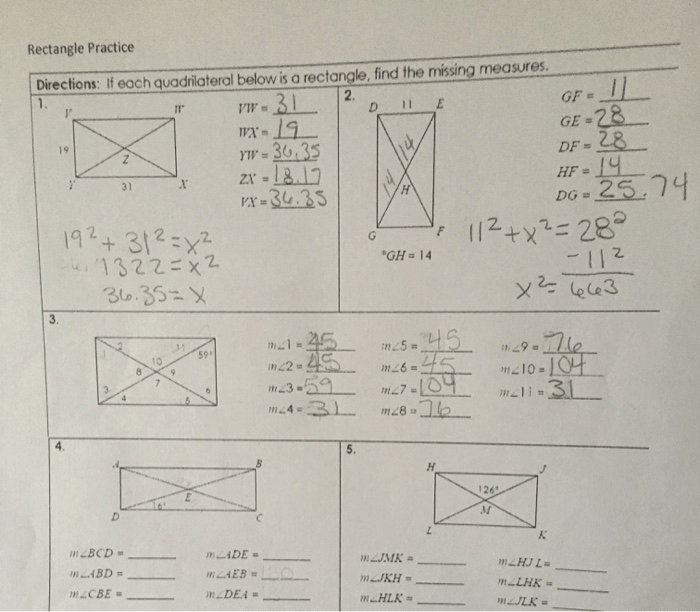
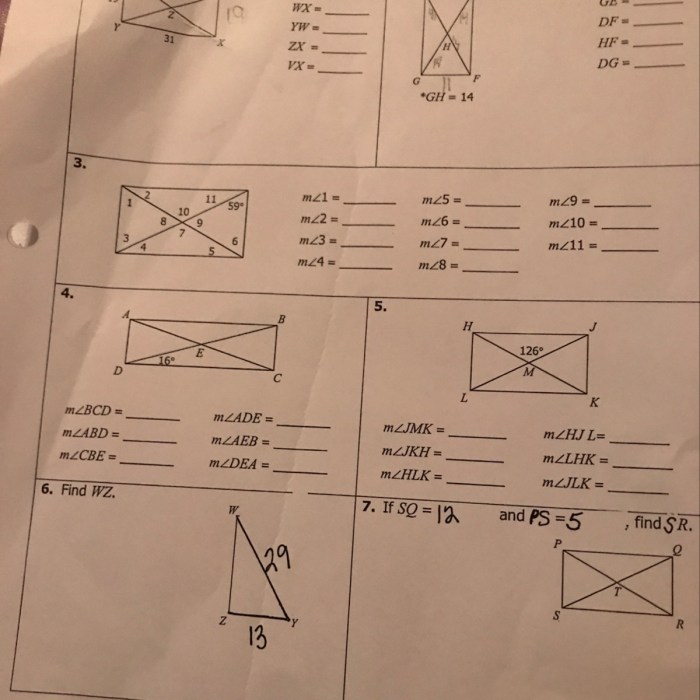
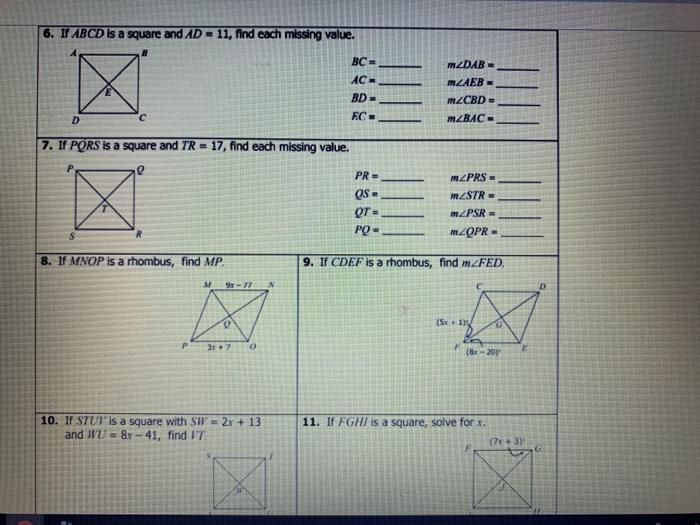
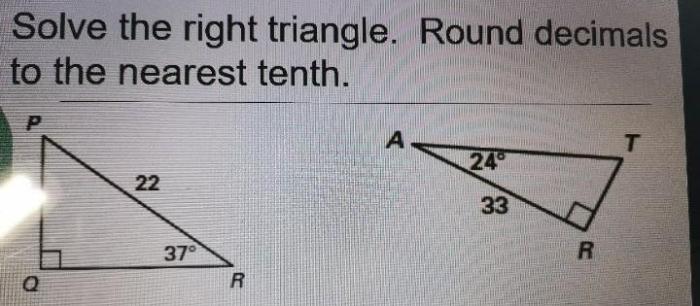
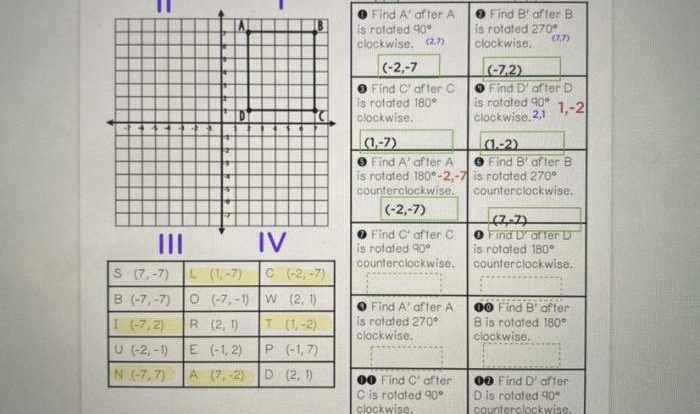
If each quadrilateral below is a rectangle, we embark on a captivating journey into the realm of geometry, where we unravel the defining characteristics of this ubiquitous shape, its classification, and its myriad applications in the world around us.
Delving into the intricacies of quadrilaterals, we establish the foundational concepts, meticulously examining the properties that distinguish rectangles from other polygons. Through visual representations and engaging examples, we illuminate the key features that define rectangles, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently identify and classify these shapes.
Properties of Quadrilaterals: If Each Quadrilateral Below Is A Rectangle
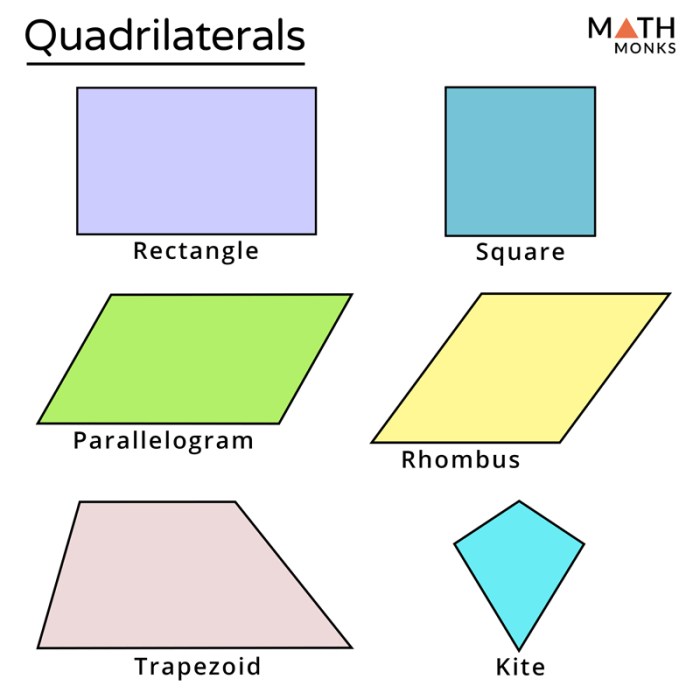
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides and four angles. The key characteristics of a quadrilateral are:
- Opposite sides are parallel.
- Opposite angles are equal.
- The sum of the interior angles is 360 degrees.
A rectangle is a quadrilateral with four right angles. The defining properties of a rectangle are:
- All four sides are equal in length.
- All four angles are right angles.
- The diagonals are equal in length and bisect each other.
Identifying Rectangles
To determine whether a quadrilateral is a rectangle, the following criteria must be met:
- The opposite sides are parallel.
- The opposite angles are equal.
- The diagonals are equal in length and bisect each other.
If all three of these criteria are met, then the quadrilateral is a rectangle.
Quadrilateral Classification, If each quadrilateral below is a rectangle
| Quadrilateral Type | Defining Properties |
|---|---|
| Rectangle |
|
| Square |
|
| Parallelogram |
|
| Trapezoid |
|
Visual Examples
The following illustrations show examples of rectangles and other quadrilaterals:
- Rectangle: A quadrilateral with four right angles and opposite sides parallel.
- Square: A rectangle with all four sides equal in length.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel.
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides parallel.
Geometric Relationships
In a rectangle, the following geometric relationships hold true:
- The diagonals are equal in length.
- The diagonals bisect each other.
- The Pythagorean theorem can be used to find the length of the diagonals.
Applications of Rectangles
Rectangles are used in a wide variety of practical applications, including:
- Architecture: Rectangles are used in the design of buildings, rooms, and other structures.
- Engineering: Rectangles are used in the design of bridges, roads, and other infrastructure.
- Design: Rectangles are used in the design of logos, posters, and other visual materials.
FAQ
What are the key characteristics of a rectangle?
Rectangles are quadrilaterals with four right angles and four equal sides.
How can I determine if a quadrilateral is a rectangle?
Check if the quadrilateral has four right angles and four equal sides.
What are some real-world applications of rectangles?
Rectangles are used in architecture, engineering, design, and many other fields.