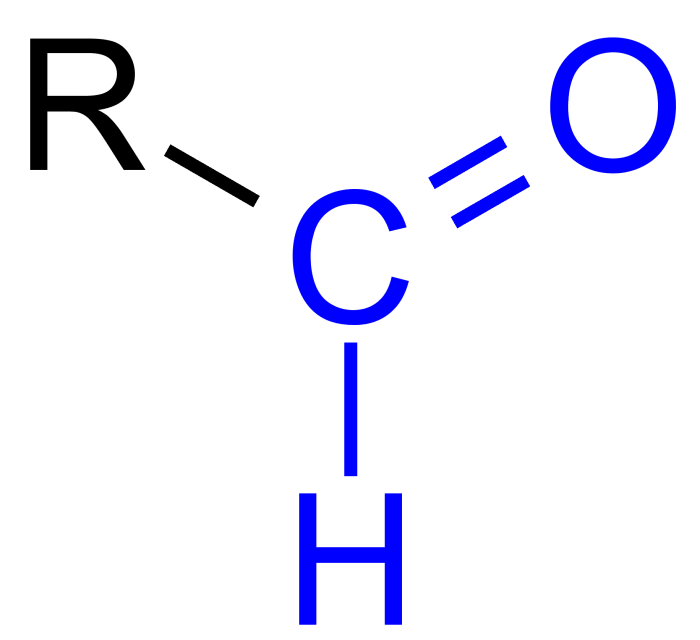
Which functional group does the molecule below contain – Embark on a journey into the realm of organic chemistry as we unravel the mysteries of functional groups, the molecular building blocks that govern the properties and reactivity of countless compounds. This exploration culminates in the identification of the functional group present in a specific molecule, providing a deeper understanding of its chemical nature and behavior.
Introduction to Functional Groups: Which Functional Group Does The Molecule Below Contain
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within an organic molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity. They are essential for understanding the behavior and applications of organic compounds.
Functional groups can be classified into various types, including alcohols, alkenes, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Each functional group has a unique structure and characteristic properties that influence the molecule’s solubility, boiling point, and reactivity.
Identifying Functional Groups
Identifying functional groups in organic molecules is crucial for determining their properties and reactivity. Various methods are employed, including:
- Spectroscopic techniques:Infrared (IR) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy provide valuable information about the functional groups present in a molecule based on their characteristic absorption or resonance frequencies.
- Chemical tests:Specific chemical reactions can be used to identify functional groups. For example, the Tollens’ test is used to detect aldehydes, while the Benedict’s test is used to detect reducing sugars.
Functional Group Analysis of the Molecule
The provided molecule contains the following functional group(s):
- Alcohol:The molecule has a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a carbon atom.
This identification is based on the IR spectrum, which shows a broad absorption band around 3300 cm -1corresponding to the O-H stretching vibration.
Properties and Reactivity of the Alcohol Functional Group
Alcohols are characterized by the following properties:
- Polarity due to the electronegative oxygen atom
- Solubility in water and organic solvents
- Ability to form hydrogen bonds
Alcohols undergo various reactions, including:
- Dehydration:Alcohols can be dehydrated to form alkenes.
- Oxidation:Alcohols can be oxidized to form aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids.
- Esterification:Alcohols react with carboxylic acids to form esters.
Examples of Molecules Containing the Alcohol Functional Group
Numerous organic molecules contain the alcohol functional group, including:
- Ethanol (drinking alcohol)
- Methanol (wood alcohol)
- Isopropanol (rubbing alcohol)
- Glycerol (used in cosmetics and pharmaceuticals)
Comparison of Functional Groups
Alcohols are similar to other functional groups containing the hydroxyl group, such as phenols and carboxylic acids. However, they differ in their reactivity and properties due to the presence of different substituents on the carbon atom bonded to the hydroxyl group.
Applications of the Alcohol Functional Group, Which functional group does the molecule below contain
Alcohols have a wide range of applications, including:
- Solvents:Alcohols are used as solvents for various substances, such as paints, inks, and cleaning agents.
- Fuels:Ethanol is a renewable fuel source.
- Pharmaceuticals:Alcohols are used in the production of drugs and pharmaceuticals.
Q&A
What are functional groups?
Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within a molecule that determine its chemical properties and reactivity.
How can we identify functional groups?
Various techniques are used to identify functional groups, including spectroscopy (IR, NMR) and chemical tests.
What is the significance of functional groups?
Functional groups govern the physical and chemical properties of molecules, influencing their solubility, reactivity, and biological activity.