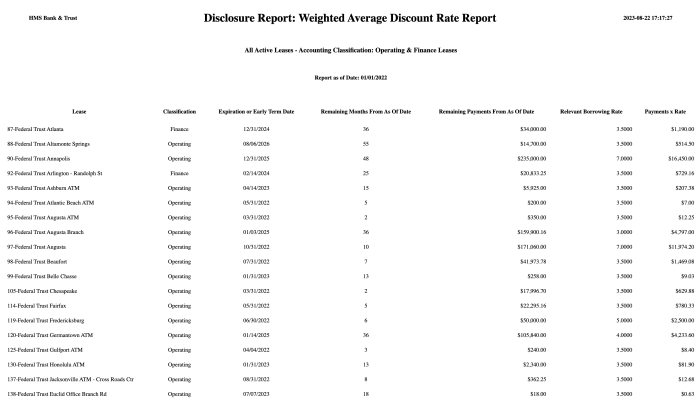
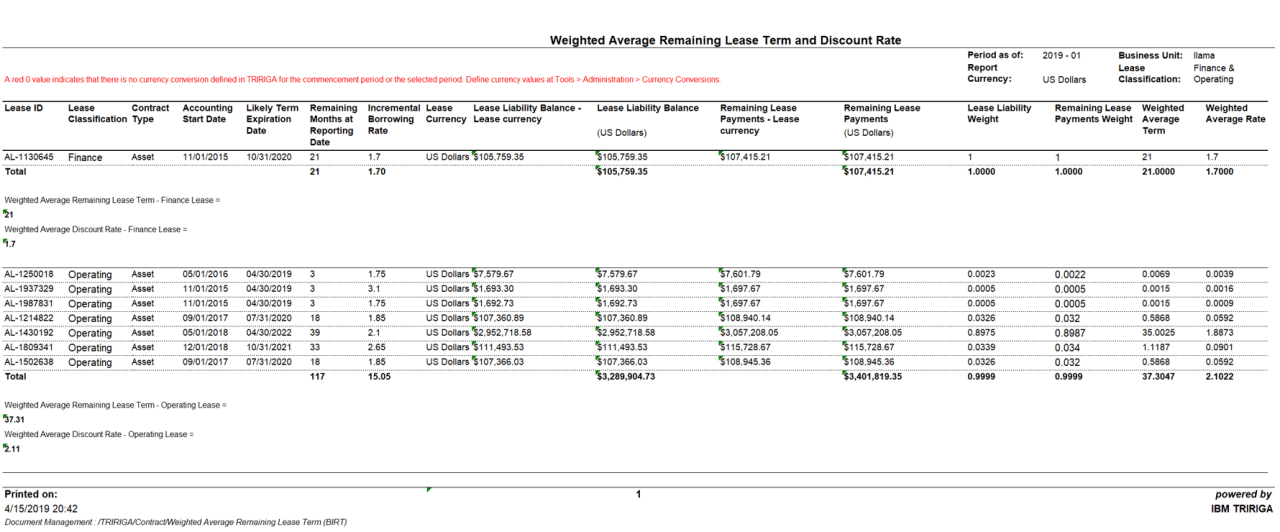
Weighted average discount rate leases (WADR leases) are a type of lease that uses a weighted average discount rate to calculate the present value of lease payments. This rate is used to determine the lease classification, which in turn affects the accounting treatment of the lease.
WADR leases are commonly used in practice, and understanding how they work is essential for accountants and financial professionals.
1. Weighted Average Discount Rate for Leases: Weighted Average Discount Rate Leases
A weighted average discount rate (WADR) is a single discount rate that is used to calculate the present value of future lease payments. It is calculated as the average of the discount rates applicable to the individual lease payments, weighted by the present value of each payment.
The purpose of using a WADR for lease accounting is to provide a more accurate representation of the cost of a lease. By using a single discount rate, the WADR eliminates the potential for distortion that can occur when different discount rates are used for different lease payments.
2. Calculation of the Weighted Average Discount Rate, Weighted average discount rate leases
The formula for calculating the WADR is as follows:
WADR = (PV1 / PV)
- R1 + (PV2 / PV)
- R2 + … + (PVn / PV)
- Rn
Where:
- PV1, PV2, …, PVn are the present values of the individual lease payments
- R1, R2, …, Rn are the discount rates applicable to the individual lease payments
- PV is the total present value of all lease payments
For example, if a lease has three annual payments of $1,000, $2,000, and $3,000, and the discount rates applicable to these payments are 5%, 6%, and 7%, respectively, the WADR would be calculated as follows:
WADR = ((1,000 / 3,333) – 5%) + ((2,000 / 3,333) – 6%) + ((3,000 / 3,333) – 7%)
WADR = 5.94%
The factors that affect the WADR include the following:
- The term of the lease
- The interest rate environment
- The creditworthiness of the lessee
- The type of lease
3. Use of the Weighted Average Discount Rate in Lease Accounting
The WADR is used to calculate the present value of lease payments for both operating leases and capital leases. For operating leases, the present value of lease payments is used to determine the lease expense that is recognized in the income statement.
For capital leases, the present value of lease payments is used to determine the carrying value of the leased asset that is recognized on the balance sheet.
The WADR can also impact the classification of a lease. If the WADR is less than the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate, the lease is classified as an operating lease. If the WADR is greater than or equal to the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate, the lease is classified as a capital lease.
For example, if a lessee has an incremental borrowing rate of 6% and the WADR for a particular lease is 5.94%, the lease would be classified as an operating lease.
4. Advantages and Disadvantages of Using a Weighted Average Discount Rate
There are several advantages to using a WADR for lease accounting. These advantages include the following:
- It provides a more accurate representation of the cost of a lease.
- It eliminates the potential for distortion that can occur when different discount rates are used for different lease payments.
- It is relatively easy to calculate.
There are also some disadvantages to using a WADR. These disadvantages include the following:
- It can be difficult to determine the appropriate discount rates to use.
- It can be time-consuming to calculate the WADR, especially for complex leases.
- It may not be appropriate for all leases.
A WADR is most appropriate for leases that have a relatively short term and that are not subject to significant interest rate risk.
5. Alternatives to Using a Weighted Average Discount Rate
There are several alternatives to using a WADR for lease accounting. These alternatives include the following:
- Incremental borrowing rate method:This method uses the lessee’s incremental borrowing rate as the discount rate for all lease payments.
- Specific borrowing rate method:This method uses a specific borrowing rate that is obtained from a lender for the purpose of financing the lease.
- Rate implicit in the lease:This method uses the rate that is implicit in the lease contract.
The specific circumstances under which each method should be used are as follows:
- The incremental borrowing rate method should be used when the lease is not subject to significant interest rate risk.
- The specific borrowing rate method should be used when the lease is financed with a specific loan.
- The rate implicit in the lease method should be used when the lease is not subject to significant interest rate risk and the rate implicit in the lease is reasonable.
Key Questions Answered
What is a weighted average discount rate (WADR)?
A WADR is a rate used to calculate the present value of lease payments. It is a weighted average of the interest rates of the lessor’s outstanding debt.
How is the WADR used in lease accounting?
The WADR is used to calculate the present value of lease payments, which is then used to determine the lease classification.
What are the advantages of using a WADR?
The advantages of using a WADR include simplicity, consistency, and comparability.
What are the disadvantages of using a WADR?
The disadvantages of using a WADR include potential inaccuracy and the need for estimation.