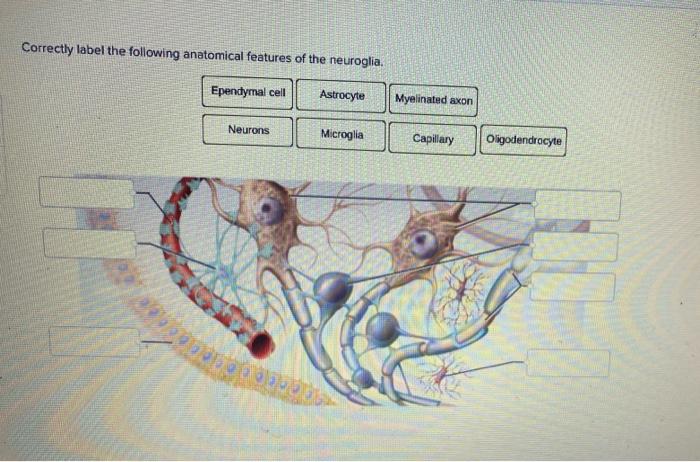
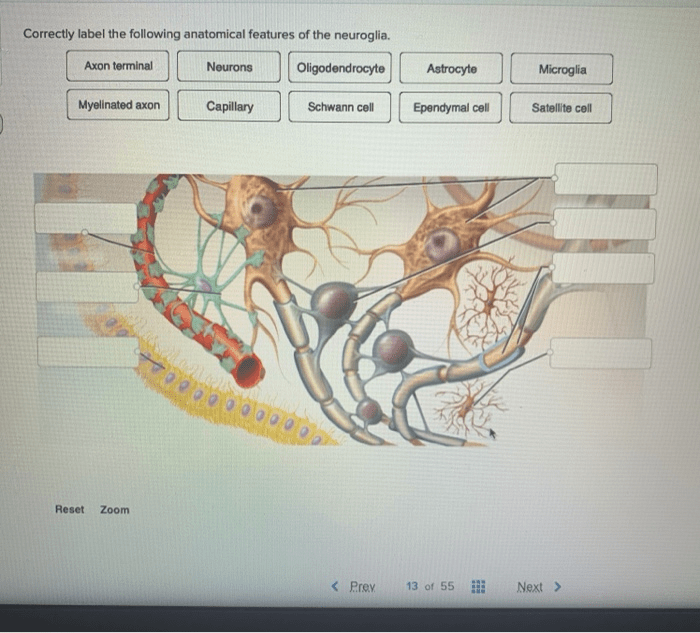
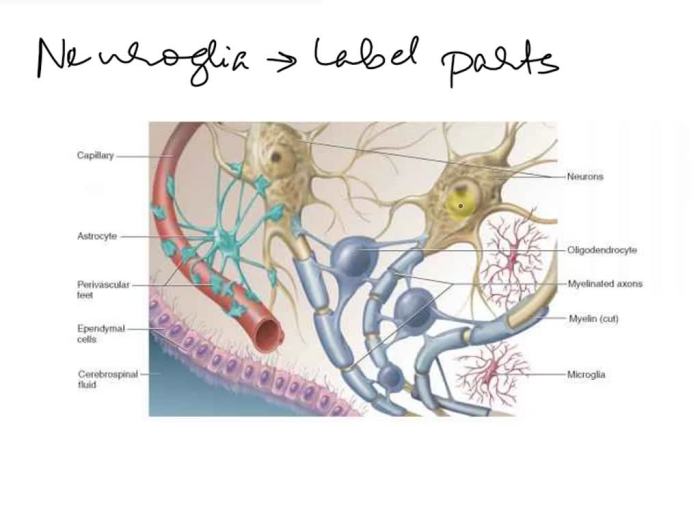
Correctly label the following anatomical features of the neuroglia. – Correctly labeling the anatomical features of neuroglia is crucial for understanding the intricate workings of the nervous system. Neuroglia, often referred to as glial cells, are the non-neuronal cells that provide structural and functional support to neurons, the primary information-processing units of the brain and spinal cord.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the various types of neuroglia, their unique morphology, and their essential roles in maintaining homeostasis, supporting neuronal function, and contributing to the overall health and functionality of the nervous system.
Anatomical Features of Neuroglia
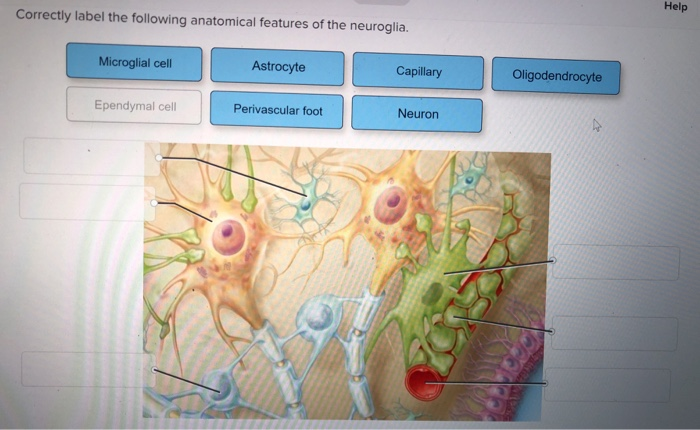
Neuroglia, also known as glial cells, are non-neuronal cells that constitute approximately 90% of the central nervous system (CNS) and 50% of the peripheral nervous system (PNS). They play a crucial role in supporting and maintaining the function of neurons, the primary functional cells of the nervous system.
Types of Neuroglia
- Astrocytes: Star-shaped cells that are the most abundant type of neuroglia in the CNS. They maintain the blood-brain barrier, provide structural support, and regulate ion homeostasis.
- Oligodendrocytes: Cells that produce myelin sheaths, which insulate axons in the CNS. This insulation allows for faster transmission of electrical signals.
- Microglia: Phagocytic cells that act as the resident immune cells of the CNS. They remove cellular debris, pathogens, and damaged neurons.
- Ependymal cells: Cells that line the ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord. They produce cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste products.
- Schwann cells: Cells that produce myelin sheaths around axons in the PNS. They are similar to oligodendrocytes but have a different morphology and are found only in the PNS.
Role of Neuroglia, Correctly label the following anatomical features of the neuroglia.
Neuroglia play a vital role in the function of the nervous system:
- Structural support: Neuroglia provide physical support to neurons and help maintain the overall architecture of the nervous system.
- Metabolic support: Neuroglia supply nutrients to neurons and remove waste products.
- Electrical insulation: Myelin sheaths produced by oligodendrocytes and Schwann cells insulate axons, increasing the speed and efficiency of electrical signal transmission.
- Homeostasis maintenance: Neuroglia regulate the ionic balance and pH of the extracellular fluid, ensuring optimal conditions for neuronal function.
- Immune defense: Microglia act as the immune cells of the CNS, protecting against infection and injury.
Question & Answer Hub: Correctly Label The Following Anatomical Features Of The Neuroglia.
What is the primary function of neuroglia?
Neuroglia provide structural and functional support to neurons, maintaining homeostasis, facilitating neuronal communication, and contributing to the overall health of the nervous system.
How many types of neuroglia are there?
There are several types of neuroglia, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and Schwann cells, each with distinct morphology and specialized functions.
Why is it important to correctly label the anatomical features of neuroglia?
Correctly labeling neuroglia allows researchers and clinicians to accurately identify and study these cells, contributing to our understanding of their roles in both normal and pathological conditions.